Chikungunya Virus- What Do You Need To Know?
Last updated on : 07 Mar, 2025
Read time : 11 min
What is Chikungunya?
Chikungunya, which literally means “to become contorted” in reference to the stooped appearance of those suffering from joint pain, is a virus that is spread to humans by the bites of mosquitoes infected with the virus. Chikungunya is caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), an alphavirus. Mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, are responsible for transmitting the virus. It is important to note that this disease does not spread from person to person through bodily contact or saliva.
Where is Chikungunya Prevalent?
Chikungunya is commonly found in tropical regions of Africa and Asia, where it has become a significant public health problem. Endemic areas include parts of India, Southeast Asia, and several African countries. In recent years, there have been outbreaks in temperate regions, such as Europe and the Americas, due to the colonization of Aedes mosquitoes in these areas.
Chikungunya Causes
Chikungunya is primarily caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), which is transmitted through Aedes mosquitoes. Environmental factors and regions where these mosquitoes thrive play a significant role in the spread of the virus.
A. Mosquito-borne Virus
Humans are exposed to the chikungunya virus when an infected Aedes mosquito bites them. The main hosts of the virus during an outbreak are humans. The mosquito becomes infected when it bites a person who already has the virus, continuing the transmission cycle.
B. Environmental Factors and Regions
Aedes mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, thrive in tropical and subtropical regions. These mosquitoes breed in stagnant water and are most active during daylight hours. Regions with warm climates and high humidity, such as parts of Africa, Asia, and the Indian subcontinent, are particularly susceptible to outbreaks.
C. Other Factors
- Similar Viruses: Dengue, Zika, and chikungunya viruses are all spread by mosquitoes and have similar clinical symptoms, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment.
- Blood Transmission: The chikungunya virus can be transmitted through blood. Medical professionals who draw blood from infected patients and laboratory workers handling infected blood are at risk.
- Mother-to-Child Transmission: Infected mothers can transmit the virus to their newborns during preterm deliveries. Research indicates a higher chance of abortion or fetal death if the mother is infected before the 22nd week of pregnancy. Symptoms in newborns can include fever, pain, poor feeding, and skin alterations, with severe cases leading to viral meningoencephalitis.
Government Reporting: It is crucial for doctors to report suspected chikungunya cases to state or local health departments to help with diagnosis and reduce the risk of local transmission.
Additional Read: Home remedy for dengue
Symptoms of Chikungunya
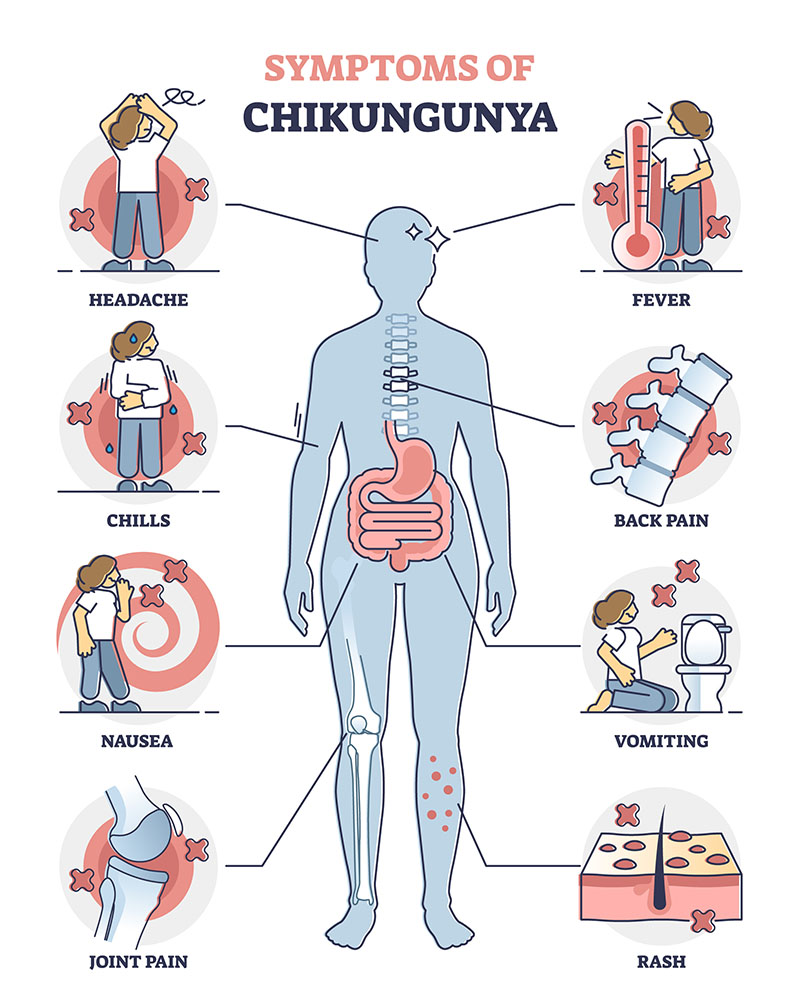
The most common symptoms of chikungunya include fever and joint pain. Additional symptoms may involve headaches, vomiting, nausea, back pain, and skin rashes. Chikungunya symptoms can be divided into two stages: acute and chronic. Let’s delve into each stage in detail.
Acute Stage
Adults who are sick often feel very tired, lose their appetite, have muscle pain, get sick, and throw up. They may also feel confused for a short time. The first ten days after the disease starts are called the acute stage.
- High fever, joint pain, back pain, and headaches are the most common symptoms.
- Fever is usually high (typically > 39 °C [102 °F]), and antipyretics don’t help much.
- Adults who are sick often feel very tired, lose their appetite, have muscle pain, feel sick, and throw up.
- Elderly people who are sick sometimes feel confused for a short time.
- Peripheral joints, particularly interphalangeal joints, wrists, and ankles, are frequently painful and swollen.
- Some patients may also have a temporary maculopapular rash on their face and trunk that is sometimes swollen and itchy.
- Symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract are common.
Chikungunya’s high fever is a key symptom that is also commonly observed in viral fevers. If you are experiencing such symptoms, it’s important to learn more about viral fever symptoms to better understand and manage your condition.
Chronic Stage
- Within the first three months, most patients have generalised pain and inflammation in the joints and tendons within the first three months.
- Walking and object-handling difficulties can induce
- Rheumatism caused by CHIKV is the most common manifestation of the chronic stage.
Read more– Home Remedies for Joint Pain
Diagnosis of Chikungunya
A. Blood test
The standard way for a lab to diagnose a virus is to test serum or plasma for the virus, viral nucleic acid, virus-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) M, and virus-neutralizing antibodies.
A viral culture may identify the virus during the first three days of sickness. Serum frequently contains the chikungunya virus RNA.
So, patients whose samples were taken during the acute phase and came back negative should have samples taken during the convalescent phase (the later stage of an infectious disease or illness) to rule out the diagnosis for sure.
Some of the lab findings are:
- Leukopenia is characterised by a decrease in the number of white blood cells in the blood.
- Mild thrombocytopenia is a deficiency of platelets in the blood.
- A slight increase in C-reactive protein: The liver produces the protein known as C-reactive protein (CRP). When there is inflammation in the body, CRP levels rise.
- Hepatic cytolysis: This condition is frequently the result of the synthesis of reactive metabolites through the cytochrome P450 system that target the liver’s structural elements and can cause harmful immune allergic reactions or autoimmune hepatitis.
- Lymphopenia is a condition in which your blood does not contain enough white blood cells, known as lymphocytes.
B. Physical exam
- On the first x-rays of the hands and feet, half of the patients might have erosions and/or joint space narrowing.
- People have also talked about other types of joint destruction, such as severe relapses of psoriatic arthritis that had been under control, enteropathies, and periostitis.
- MRI scans seem to be able to pick up early changes in the joints and tendons caused by rheumatism caused by CHIKV.
Treatment of Chikungunya
Chikungunya treatment involves:
- Unfortunately, no antiviral medication has been shown to be effective against human CHIKV infection.
- As a result, only painkillers and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat the acute stage (NSAIDs).
- Acetaminophen is the preferred medication. Because of the risk of bleeding, aspirin should be avoided. For additional information on dietary recommendations during recovery, refer to Chikungunya diet.
Prevention of Chikungunya
- There is currently no commercial CHIKV vaccine available. Because of the potential for viral persistence.
- Avoid travelling to regions where epidemics (disease outbreaks) are still active.
- Keeping windows and doors closed and staying indoors during peak mosquito activity times
- Reduce standing water.
Wear Protective Clothing
- Cover up with long sleeves and pants.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothes will help prevent bites by keeping your skin covered with sweat, which helps keep mosquitoes away from you as much as possible.
- When you go outside in the morning or evening (when mosquitoes are most likely to be out), wear clothes treated with permethrin.
- A chemical insecticide called permethrin can be used to coat clothing, shoes, bed nets, and camping supplies to kill or deter insects like mosquitoes and ticks.
- Use insect and mosquito repellents.
Conclusion
If you think you have been infected with the chikungunya virus, contact your healthcare provider right away so that they can determine if you need treatment or monitoring for signs of disease progression. You can get both brand-name and generic drugs by uploading your prescription to the Truemeds app. When you order medicines online, you may save money by choosing an alternative or generic medicine suggested by Truemed’s expert doctors. You can save up to 72% on your purchase and get free home delivery across India.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Most of the time, the antibody levels can be seen in the first week after the illness starts and stay that way for about two months.
Chikungunya deaths are extremely rare. People who are older or who have long-term diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic kidney failure, tuberculosis, or HIV should see a doctor to get a more thorough diagnosis and check on their health.
The critical difference between the two infections is that chikungunya has a higher fever and more severe joint pain. Chikungunya pain can be severe (bend people over), affecting their hands, feet, knees, and back. This makes it difficult to walk or even to open a water bottle. It’s vital to watch for warning symptoms since dengue can lead to consequences after the fever goes down.
A chikungunya PCR test is a diagnostic method that detects the genetic material of the chikungunya virus in a patient’s blood. This test helps confirm the presence of the virus during the early stages of infection.
Chikungunya symptoms, such as chikungunya fever and joint pain, typically last for 7 to 10 days. However, joint pain and fatigue can persist for weeks to months in some cases.
The fastest way to manage chikungunya at home involves plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and taking pain relievers like acetaminophen for fever and joint pain. There is no specific cure for chikungunya, but supportive care helps alleviate symptoms.
No, chikungunya is not contagious. The virus cannot be transmitted from person to person through direct contact, saliva, or bodily fluids.
No, chikungunya cannot be transmitted from person to person. It is primarily spread through the bites of infected Aedes mosquitoes.
A chikungunya rash is a common symptom that appears as red spots or blotches on the skin. It usually occurs along with fever and joint pain during the infection.
Yes, you can eat eggs during chikungunya. Eggs are a good source of protein and nutrients that can support the body’s recovery.
Chikungunya supportive therapy involves managing symptoms with rest, hydration, and pain relievers. There is no specific antiviral treatment, so supportive care focuses on alleviating fever, joint pain, and other symptoms.
Chikungunya fever typically lasts for 2 to 7 days. However, joint pain and other symptoms may persist for longer periods.
Yes, chikungunya can cause long-term health issues. Some patients experience persistent joint pain, arthritis, and fatigue for months after the acute phase of the infection.
Currently, there is no approved vaccine for chikungunya. Prevention focuses on avoiding mosquito bites and controlling mosquito populations.
Supportive care for chikungunya patients includes rest, staying hydrated, and using pain relievers like acetaminophen. It is essential to avoid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) until dengue fever is ruled out to prevent complications.
Disclaimer: This information shouldn’t be used to diagnose or treat a medical condition, nor should it be used in a medical emergency. A qualified medical professional should be consulted to diagnose and treat all medical conditions.
References-
- Chikungunya Virus | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Retrieved January 4, 2023, from https://www.cdc.gov/chikungunya/index.html
- Chikungunya fact sheet 2022 (December 8) Chikungunya Fact Sheet Retrieved January 4, 2023, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chikungunya
Disclaimer
Our healthcare experts have carefully reviewed and compiled the information presented here to ensure accuracy and trustworthiness. It is important to note that this information serves as a general overview of the topic and is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose, prevent, or cure any health problem. This page does not establish a doctor-patient relationship, nor does it replace the advice or consultation of a registered medical practitioner. We recommend seeking guidance from your registered medical practitioner for any questions or concerns regarding your medical condition.
Popular Articles
Recommended Articles
Recent Articles
Top-Selling Medicines:
...View more
Top-Selling OTC:
...View more
Subscribe
Registered Office Address
Grievance Officer
Download Truemeds

Contact Us
Our customer representative team is available 7 days a week from 9 am - 9 pm.
v3.7.5
Our Payment Partners


























































